Systems engineering indisputably stands as an exceptional career choice for anyone with a penchant for problem-solving and holistic design. With continuous advancements in technology, the demand for skilled system engineers is projected to rise, providing compelling career stability. The profession not only offers great remuneration but also a golden opportunity to influence the development of complex, multidimensional systems, placing you at the forefront of technological innovation. It’s indeed both exciting and rewarding!
Table of Contents
- Understanding Systems Engineering
- Enhance Your Systems Engineering Mastery
- What Markets do Systems Engineers Work in?
- Aircraft Systems
- Automotive Systems
- Healthcare: Medical Systems
- Healthcare IT Systems
- Telecommunications: Network Systems
- Telecom Infrastructure
- Defence: Weapons Systems
- Military IT Systems
- Railway Train Control Systems
- Railway Infrastructure
- Railway Communication and Information Systems
- Rail Vehicle Engineering
- The Future of Systems Engineering
- Academic Pathways
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What does a Systems Engineer do?
- 2. Is Systems Engineering in demand?
- 3. What skills does a Systems Engineer need?
- 4. What’s the average salary of a Systems Engineer?
- 5. What are the career advancement opportunities for a Systems Engineer?
- 6. Is a degree required to become a Systems Engineer?
- 7. Is Systems Engineering difficult?
- 8. How does Systems Engineering benefit businesses?
- 9. Where do Systems Engineers work?
- 10. What are some significant challenges Systems Engineers face?
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Systems Engineering
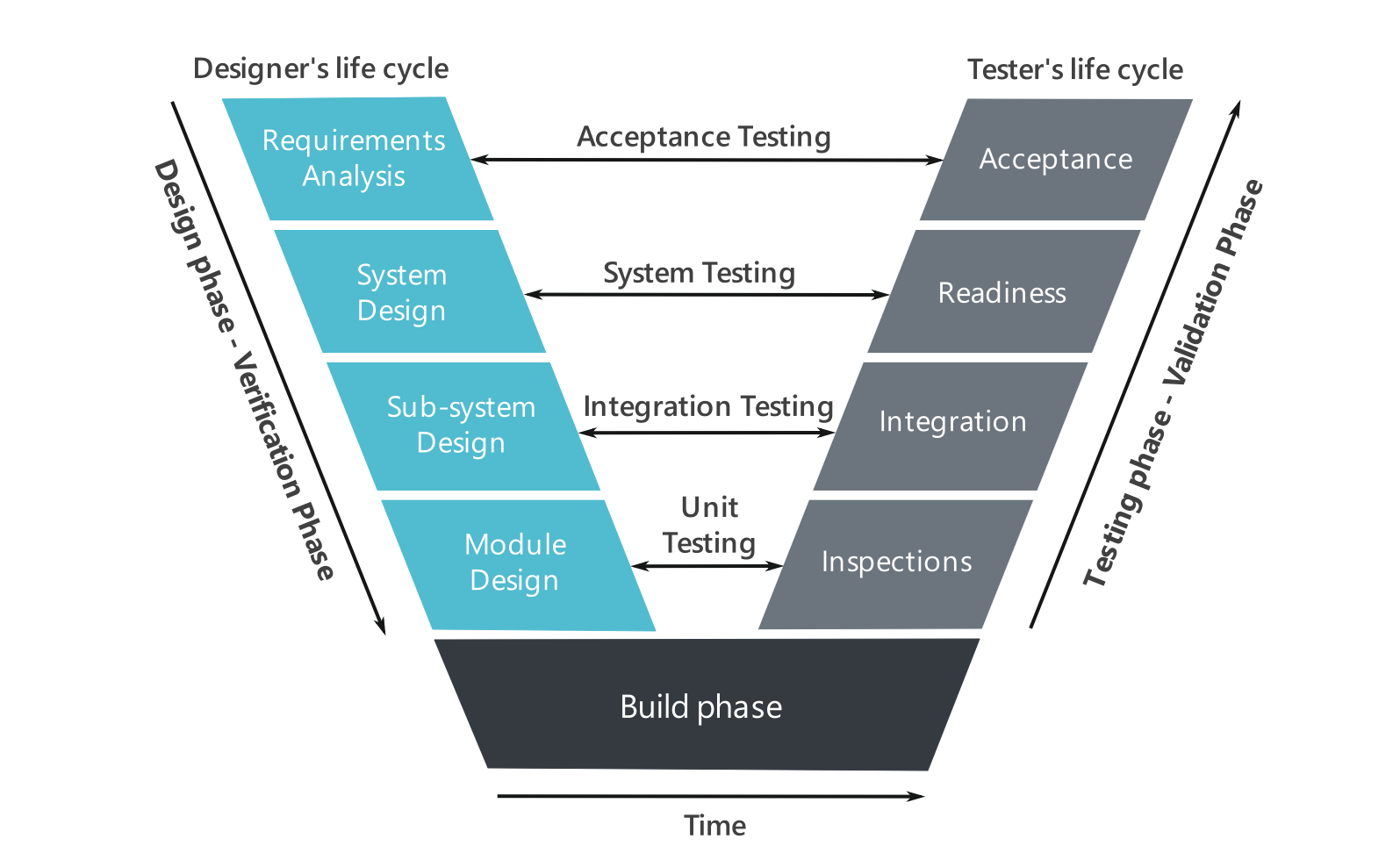
Systems engineering is the comprehensive course of action that covers the entire lifecycle of a system – from inception and design to deployment and maintenance. This discipline converges the realms of software, hardware, networking, and process engineering with a central unifying focus – to ensure the coordination of different subsystems towards the attainment of the main operational goals. This all-inclusive viewpoint presents unparalled complexity and breadth which is both challenging and fulfilling.
Enriching Collaboration
Systems engineers typically work in teams composed of professionals from a variety of disciplines. This entails the need for these engineers to have excellent communication, collaboration, and diplomacy skills to navigate different viewpoints and reach a consensus in decision making. System engineering, therefore, not only builds your technical acumen but also equips you with significant soft skills. The multidisciplinary nature of the work brings with it a distinctive and exciting organisational dynamic.
Design and Systems Integration
At the heart of systems engineering is system design – formulating an operational system capable of achieving the required functionality while optimising performance parameters. This process involves requirements analysis, system synthesis, validation, and verification. Additionally, one chief responsibility of systems engineers is to manage the integration and configuration control of all these subsystems. This complex juggling act is undeniably challenging, yet it provides an unmatched sense of accomplishment once done correctly.
Enhance Your Systems Engineering Mastery
For those who are eager to augment their knowledge in systems engineering, embarking on online courses is a strategic step forward. Whether you are ascending the career ladder or are a novice diving into this demanding yet rewarding field, equipping yourself with specialised knowledge is paramount. Fortunately, the digital world has brought forth education within our arm’s reach. A variety of top-tier online Systems Engineering courses are awaiting your exploration.
Among a plethora of options, choosing the right course might seem like finding a needle in a haystack. Thus, the guide at Req.io offers its assistance. This comprehensive guide meticulously reviews and ranks the top 10 online Systems Engineering courses, catering to an array of interests such as software engineering, network design, cybersecurity and more. The guide further cherry-picks the crème de la crème, listing the top 4 highly recommended courses.
Sharpen your professional capabilities and unlock your potential with these immersive courses. It’s time to embrace the flexibility and convenience of online learning for your professional ascension. To explore these courses, head over to this guide.

What Markets do Systems Engineers Work in?
When pondering on the notion of system engineering, one might find it challenging to envision the scope of its applications. However, you will astoundingly discover, system engineers are vital forces in array of sectors, from transportation, healthcare to telecommunications and defence. With their diverse and crucial roles, they are indeed the catalysts for modern technological marvels. To cultivate a deeper understanding of these arenas, let us delve into four key marketing areas where system engineers predominantly operate.
Aircraft Systems
System engineers play an integral part in the aviation industry, where they design and manage complex aircraft systems. From onboard computer systems, navigation instruments to propulsion machinery, system engineers are pivotal in ensuring optimal performance and safety. They also liaise with different teams to develop and implement risk management plans, addressing possible system failures. In addition, system engineers can precisely foresee the overarching impacts of individual component modifications on the system, a crucial factor in aerospace design.
Automotive Systems
In the automotive industry, system engineers manipulate electronic control units, navigation systems, security features, and more. Leveraging their skills, they oversee the creation of reliable, efficient vehicles intricately designed to deliver enhanced user experience while upholding road safety standards. With the advent of electric and autonomous vehicles, opportunities for system engineers in this sphere are set to skyrocket. Proactively involving in ground-breaking projects, they are essential to the realisation of future transportation.
Healthcare: Medical Systems
In the healthcare industry, system engineers play a substantial role in integrating technological advancements with medical practices, creating dynamic medical systems. They are central to the design, development, and implementation of biomedical equipment, electronic medical record systems, telemedicine, and machine learning applications. Thus, improving patient care, record accuracy and overall operational efficiency of the medical field. Their principle is to design systems that ensure the utmost patient safety while revolutionising healthcare delivery.
Healthcare IT Systems
System engineers are also the backbone of Healthcare IT departments; they design and maintain expansive network infrastructures, manage healthcare databases, and safeguard sensitive patient data. With growing dependencies on technology, the need for system engineers who can master the art of technological integration with healthcare functions has become paramount. Besides the technical aspect, they understand the industry’s regulatory environment, making them proficient in addressing unique industry concerns and its complex needs.
Telecommunications: Network Systems
In the telecommunications sector, system engineers design, optimise, and manage telecommunication systems and networks. They ensure seamless transmission and reception of signals, dealing with broadband, voice over IP (VoIP), instant messaging, and videoconferencing systems. With the enforcement of new technologies like 5G, IoT, system engineers are brewing to confront formidable challenges while at the same time, experiencing noteworthy professional growth.
Telecom Infrastructure
System engineers also partake in developing and maintaining infrastructure that supports these telecommunications services. From transmitter stations to satellites, these engineers help in designing resilient and adaptive infrastructure to optimise signal availability, capacity, and quality. Their work is behind the seamless streaming of online content, uninterrupted phone calls, and high-speed internet that we relish today.
If you're eager to transition into systems engineering from another industry, remember this crucial tip: leverage your unique background. Your varied perspective can foster diverse solutions that traditional thinking might overlook. Enrich your technical skills with a focused course or qualification, but don't underestimate the value of your past experiences. As an industry newcomer, you may well hold the key to innovative problem-solving in the realm of systems engineering.
Defence: Weapons Systems
In the defence sector, system engineers are invincible elements of weapons system development, from ballistic missile defence systems to next-generation fighter planes. They are entrusted with the daunting task of designing systems that defend nations. Their multifaceted roles involve assessing system risks, strategising responses, and crafting efficient, effective defence mechanisms while adhering to stringent safety protocols.
Military IT Systems
Moreover, system engineers are the linchpins of defence-oriented IT, managing secure communication networks and confidential databases. They are legal custodians of critical defence data infrastructure and are habitually engaged in countering cyber threats. Their primary objective is to empower defence forces with robust, secure, and efficient IT systems, facilitating precise communication and decision-making.
In conclusion, the role of system engineers spans across various sectors, marking their indispensable footprint in shaping today’s technology landscape. The ample opportunities and diverse fields for system engineers undoubtedly reiterate that it is a rewarding career to venture into.
Railway Train Control Systems
In the realm of railways, system engineers are crucial in the development and management of advanced train control systems. From signalling systems to automated train operations, these professionals are responsible for maintaining a seamless, safe, and fast railway service. They relentlessly work on designing and system testing, to comprehensively eliminate potential issues, ensuring a fault-free operation. Their in-depth system understanding facilitates effective decision-making, meeting future demands, and strategic planning for network expansion.
Railway Infrastructure
System engineers working in railway infrastructure focus on the design, implementation, and maintenance of critical railway elements such as tracks, power supply systems, tunnel ventilation, and bridges. They are responsible for the optimisation of the network’s efficiency and safety from a systemic perspective. Their expertise allows for considerations of future improvements and adjustments, enabling adaptive responses to changes and challenges in the railway sector.
Railway Communication and Information Systems
Communication and IT systems in railways are another domain where system engineers exhibit their mastery. They design communication systems to facilitate the efficient spontaneous exchange of information between trains, control centres, and stations. Their duties extend to managing databases, developing secure ticketing systems, and advancing railway digital solutions. By prioritising security and reliability, system engineers play a paramount role in magnifying the convenience and surety of railway users.
Rail Vehicle Engineering
Lastly, in rail vehicle engineering, system engineers are engaged in the design, manufacture, and maintenance of various types of rail vehicles – from freight wagons to high-speed passenger trains. They harmoniously combine different subsystems – structural elements, propulsion systems, brake systems, and more, ensuring the end product meets stringent safety, performance, and comfort standards. Their efforts significantly contribute to the evolution, modernisation, and higher safety records of today’s railway systems.

The Future of Systems Engineering
The progress of technology and the rising reliance on intricate systems in sectors such as aerospace, defence, telecommunications, computing, and infrastructure signify a bright future for systems engineering. This surge in demand heralds increased job security and progression opportunities for burgeoning system engineers. Additionally, these varied sectors also promise an array of interesting projects, ensuring that boredom is a stranger in this profession.
Continuous Learning
Given the dynamic landscape of technology, a static knowledge-base is an obsolete notion in the realm of systems engineering. This profession demands continuous learning to keep up with the latest state-of-the-art technologies, methods, and management practices. This constant intellectual growth is fantastic for those who love to learn and innovate, making systems engineering incredibly fulfilling.
Academic Pathways
Embarking on a career in systems engineering generally requires a degree in systems engineering, computer science, or a related discipline. Specialisation programs or further studies in a specific area, such as network engineering or software development, can enhance your employability and accelerate career progress. Notably, many engineers transition into the field from other engineering sectors and accumulate systems-based knowledge through experience.
Professional Certification
Further to an academic degree, obtaining a professional certification can also provide a competitive edge in the job market. Certifications such as those offered by the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) or the Systems Engineering Professional Certification by NASA can enhance your credibility and marketability as a systems engineer. These courses not only add to your theoretical learning but also serve as a practical training ground, bringing real-world, hands-on experience to your resume.
Consider this: As an aspiring system engineer, never shy away from network building. Engage with industry forums, online communities, or local events. These platforms offer treasures of knowledge, anecdotes, and unique problem-solving approaches. Moreover, they sometimes open doors to mentorship, internships, or job opportunities. Remember, in the world of systems engineering, growing your knowledge is as much about textbook studies as it is about hands-on experience and insights gained from industry peers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does a Systems Engineer do?
System engineers tackle complex projects by pinpointing stakeholder needs, exploring various solutions, articulating system requirements, and leading the system development lifecycle. They prolifically manage the integration of different elements into a well-orchestrated, efficient, and adaptable system. Additionally, they ensure system viability from both technical and business perspectives, thus serving as the cornerstone of successful, multifaceted projects.
2. Is Systems Engineering in demand?
Unquestionably, systems engineering is in high demand. In an era burgeoning with technological breakthroughs, industries are hunting for adept systems engineers to tackle increasingly intricate projects. Their power in designing large-scale systems seamlessly addressing various requirements drives their market value. From transport, healthcare to telecommunications, their expertise is sought after, making systems engineering a booming profession.
3. What skills does a Systems Engineer need?
A proficient systems engineer manifests robust technical ability, analytical acumen, strategic problem-solving skills, and extraordinary attention to detail. They exemplify excellent communication and leadership traits, efficiently juggling different teams and stakeholders. Their capacity to envisage the system as a whole while focussing on individual components is indispensable. Knowledge in relevant standards, regulations, and safety requirements adds charm to their professional profile.
4. What’s the average salary of a Systems Engineer?
With the crucial role they embody, systems engineers are handsomely rewarded. Although the average salary varies significantly depending on the industry, location, and level of experience, systems engineers are highly valued. In Australia, for instance, a systems engineer can expect an average annual salary of between AU$70,000 to AU$120,000. With expertise and years of experience, these figures can reach even higher.
5. What are the career advancement opportunities for a Systems Engineer?
Stepping into the world of systems engineering opens up a wealth of career advancement opportunities. Engineers can oversee large projects, steer to managerial positions, or become specialised in a specific type of system. Since the field is diverse, ceaseless learning and upskilling can lead to more complex, rewarding roles. By demonstrating exceptional performance, system engineers can escalate to positions like Chief Technology Officer (CTO) or Director of Engineering.
6. Is a degree required to become a Systems Engineer?
Absolutely. Aspiring Systems Engineers typically require a Bachelor’s degree in systems engineering, computer science, or a related technical field. However, possessing a Master’s degree or further qualification often offers a competitive edge and can fast-track career advancement. Additionally, professional certifications such as the Certified Systems Engineering Professional (CSEP) enhance credibility in the profession and are highly valued by employers.
7. Is Systems Engineering difficult?
Discernably, systems engineering is challenging given the complexity of the systems involved and the need for integration of various multidisciplinary aspects. It demands analytical prowess, problem-solving skills, and intimate knowledge of systems and their components. However, with the correct educational background, a passion for innovation, and a continuous learning mindset, you’ll find it a challenging yet rewarding field.
8. How does Systems Engineering benefit businesses?
Systems Engineering essentially maps out a pathway for businesses to navigate complexity. It fosters robust solutions to complex problems, enhances system performance, reduces development risks, and ensures projects remain within budget and timeline. It improves product quality, enhances customer satisfaction, and gives businesses an ultimate competitive edge, thus directly contributing to business success.
9. Where do Systems Engineers work?
Systems Engineers showcase their talents in a vast array of settings. They work in technology firms, government agencies, consulting firms, and high-tech manufacturing companies, among others. Their workplace typically involves an office-setting, but they might also navigate fieldwork for systems testing, quality check or installation. Owing to their flexible skills, they can adapt to various environments, making their employment opportunities exceedingly diverse.
10. What are some significant challenges Systems Engineers face?
Managing complexity is by far the paramount challenge for Systems Engineers. They grapple with integrating diverse subsystems into a unified, co-functioning entity. Ensuring interoperability between different systems components, balancing stakeholder demands, managing project timelines and costs, and complying with safety and regulatory standards are among the other challenges they face. Despite these challenges, successful Systems Engineers use their skills and expertise to effectively steer clear through them, finding rewarding solutions.
Final Thoughts
With the astounding advancements in technology and the increasingly interlinked world we reside in, the critical role of systems engineering is unarguably profound. This compelling field presents endless opportunities to apply your technical skills, innovation, and problem-solving prowess in truly meaningful ways. The advantages it offers in terms of professional fulfilment, career growth, and financial gain are undoubtedly impressive. The breadth and depth of industries system engineers can venture into further cement its allure. So, for those armed with curiosity, motivation, and a drive to make a difference, systems engineering is indeed a fantastic career to embark upon!