In the rapidly evolving field of software and systems engineering, the management of project requirements plays a pivotal role in ensuring successful project outcomes. As projects grow in complexity, the need for a robust tool to capture, track, and manage requirements becomes undeniable. This is where IBM’s Dynamic Object-Oriented Requirements System, more commonly known as DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG), steps in as a game-changer.
DOORS NG is part of the IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management suite, designed to provide teams with comprehensive capabilities for managing project lifecycles from inception to deployment. At its core, DOORS NG facilitates better communication, collaboration, and compliance with industry standards by offering an integrated approach to requirements management. Whether you’re a systems engineer, project manager, or a member of a quality assurance team, understanding how to effectively utilize DOORS can significantly enhance your project’s success.
The aim of this beginner’s tutorial is to introduce you to the basics of DOORS Next Generation. Through this tutorial, we will cover a wide array of functionalities within DOORS NG, equipping you with the knowledge to get started on your requirements management journey.
Table of Contents
- DOORS Requirements Management Origins
- Getting Started with DOORS:
- Creating Your First Project in DOORS Next Generation
- Understanding and Working with Artifacts
- Advanced Features: Linking and Traceability
- Best Practices for Managing Links
- Navigating DOORS: Advanced Tips and Strategies
- The Path Forward: Continuing Your DOORS NG Journey
DOORS Requirements Management Origins
DOORS was originally developed by Quality Systems & Software Ltd (QSS) in the early 1990s. The tool was born out of the recognition of the need for an efficient way to manage the increasingly complex web of project requirements, especially in sectors like aerospace, defense, and telecommunications. The development was spearheaded by Tony Dodd and Dwayne Raymond, who were looking to address the challenges faced by engineers and project managers in tracking and validating requirements.
Development and Evolution
- 1991: The first version of DOORS (DOORS/1) was released. It was one of the pioneers in using a relational database to manage requirements for complex systems engineering projects.
- Mid-1990s: DOORS transitioned to a client-server model with DOORS/2, enhancing its capabilities for collaboration and access control.
- Late 1990s: The introduction of DOORS/3 brought significant improvements, including a more user-friendly graphical interface and better project management features.
Acquisition and Expansion
- 2004: Telelogic, a Swedish company specializing in software solutions for enterprise lifecycle management, acquired QSS. Under Telelogic’s stewardship, DOORS continued to evolve, incorporating more features to support enterprise-wide requirements management.
- 2008: IBM acquired Telelogic, bringing DOORS into its suite of engineering and development software solutions. This period marked significant integration with IBM’s product lineup, offering a more cohesive toolset for lifecycle management.
DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG)
- With the evolution of technology and project management methodologies, IBM introduced DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG) as part of its Rational Collaborative Lifecycle Management suite. DOORS NG represented a significant leap forward, leveraging modern web technologies and offering a more intuitive and collaborative environment for requirements management.
- DOORS NG integrated with other IBM tools like Rational Quality Manager and Rational Team Concert, providing a comprehensive solution for managing not just requirements but the entire software development lifecycle.
Recent Developments
- Present: DOORS continues to be a staple in requirements management, especially in industries where meticulous oversight of requirements is crucial. IBM frequently updates DOORS and DOORS NG, incorporating advances in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and collaboration tools to enhance its functionality and user experience.
Legacy
From its inception, DOORS has consistently adapted and evolved to meet the changing needs of its users. Its transition from a standalone tool to an integrated suite part of IBM’s broader engineering and lifecycle management offering demonstrates its enduring relevance in the field of project management. Today, DOORS is used worldwide, showcasing its adaptability and the robust foundation it provides for managing complex project requirements.
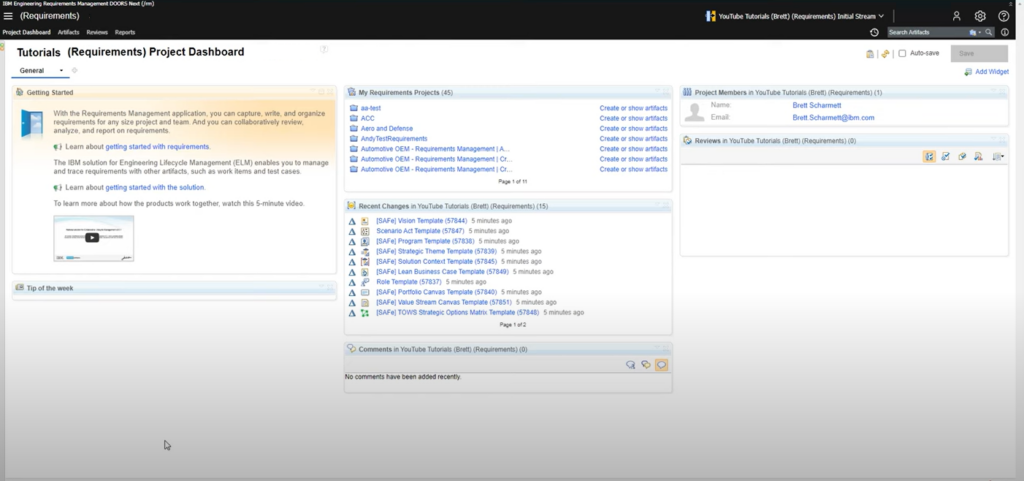
Getting Started with DOORS:
The first step into the world of DOORS NG is navigating its interface. When you log into DOORS NG, you’re greeted with what is known as the “dashboard.” If you’re familiar with social media, you can think of the dashboard somewhat like your feed – it’s where all the critical information is displayed in real-time, and it’s customizable to suit your project’s specific needs.
One of the beautiful aspects of DOORS NG is its capacity for customization right from the get-go. You can tailor the dashboard according to your preferences or project requirements by adding “widgets.” Widgets are essentially blocks on your dashboard that display different types of information or data relevant to your project. For instance, a widget could show all open requirements, test cases, or any changes made recently.
As an example, upon starting a new project from scratch, your dashboard presents a basic layout that you can then customize. Heading to the top right corner, you’ll notice an “add widget” button. Clicking on this button reveals various widgets that you can add to your dashboard. This functionality allows you to have all the necessary information you deem important at a glance.
The customization doesn’t stop at the dashboard level. DOORS NG enables you to create custom widgets for personal use, your team, or even specific project pages. This level of customization ensures that every team member can have access to the information they need, formatted in a way that makes the most sense to them.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the creation and management of artifacts, linking between artifacts for traceability, and leveraging views for data display in the upcoming sections of this tutorial.
| Step | Activities | Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Requirement Identification | Gather requirements from stakeholders. Conduct meetings and interviews. Review existing documentation. | List of initial requirements. Stakeholder consensus on requirements. |
| 2. Requirement Analysis | Analyze requirements for feasibility. Identify potential conflicts. Classify requirements (functional, non-functional). | Analyzed and categorized requirements. Documented assumptions and constraints. |
| 3. Requirement Entry | Enter requirements into DOORS NG. Define attributes for each requirement. Link related requirements for traceability. | Requirements documented in DOORS NG. Traceability links established. |
| 4. Requirement Review | Conduct review sessions with stakeholders. Update requirements based on feedback. Ensure compliance and completeness. | Reviewed and approved requirements. Record of changes and decisions. |
| 5. Requirement Verification | Define test cases linked to requirements. Conduct testing to verify requirements are met. Document test outcomes and discrepancies. | Test cases and results. Verification report. |
| 6. Requirement Validation | Validate the system against the final requirements with stakeholders. Collect acceptance from the customer or end-users. Document validation outcomes. | Validation report. Stakeholder acceptance document. |
Creating Your First Project in DOORS Next Generation
Embarking on your journey with DOORS NG begins with creating your first project – the foundational step where your requirements management process starts to take shape. This section will guide you through setting up your initial project in DOORS, an essential milestone for beginners ready to harness the capabilities of this powerful tool.
Step 1: Initiating a New Project
Once you’ve familiarized yourself with the DOORS NG dashboard, the next step is to create a new project. A project in DOORS NG serves as a container for all your related work items, such as requirements, test cases, and reports. To start, look for the “Create Project” button, typically located in a prominent place on your dashboard or within the main menu. Clicking on this button will open a dialog box or a new page where you can begin the project creation process.
Step 2: Configuring Your Project
Project Name and Description: Start by giving your project a descriptive name and a detailed description. This helps in identifying the project’s purpose at a glance and sets the stage for collaborative efforts, ensuring everyone on the team understands the project’s objectives.
Selecting a Process Template: DOORS NG may offer you the choice of process templates. These templates are designed to align with various project methodologies, such as Agile, Waterfall, or custom workflows developed within your organization. Select the one that best fits your project’s requirements engineering needs. If you’re unsure, the default template is a good starting point and can be adjusted later as you become more familiar with the tool.
Access Control: Determining who has access to your project is crucial. DOORS NG allows you to set permissions at this stage – you can choose to make the project accessible to all team members or restrict access based on roles, ensuring sensitive information is only viewable by authorized personnel.
Adding Team Members: Collaborate from the start by adding team members to your project. Enter their email addresses or usernames, and assign roles based on their responsibilities in the project. Effective team collaboration is at the heart of success in requirements management, and involving your team early sets a strong foundation for your project.
Step 3: Customizing the Dashboard
With your project now created, you’ll be directed back to your project’s dashboard. As you previously learned, dashboards in DOORS NG are highly customizable. For your new project, consider adding widgets that will display critical project metrics, outstanding tasks, recent changes, or quick access to frequently used sections of your project. This customization allows you to streamline your workflow by having all relevant information readily available, tailored to the unique needs of your project.
Step 4: Adding Your First Artifacts
Artifacts are the building blocks of your requirements management process in DOORS NG. They can represent individual requirements, specifications, use cases, and more. To add your first artifact:
- Click on the “Create” button on your project dashboard, then select “Artifact”.
- Fill in the necessary details for your artifact, such as name, description, and type (e.g., requirement, use case).
- Assign the artifact to a folder or module for organization.
- Set the artifact status, priority, and assign it to a team member if applicable.
By creating artifacts, you begin to populate your project with the essential elements that will drive its forward movement.
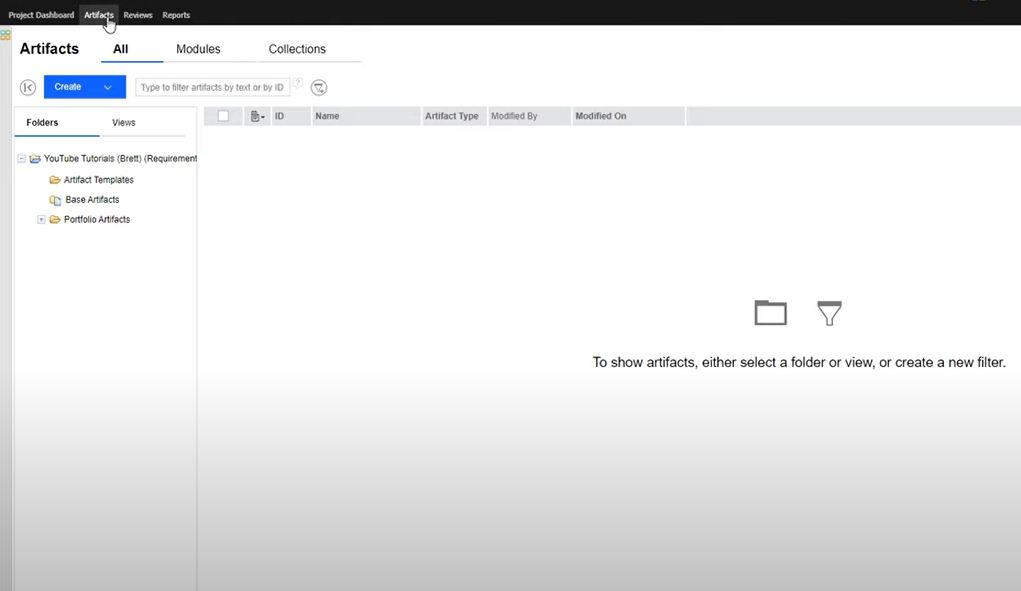
Understanding and Working with Artifacts
Once your project is up and running in DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG), it’s time to delve into the heart of requirements management: working with artifacts. Artifacts in DOORS NG represent the tangible elements of your project’s requirements, including documents, specifications, and various types of requirements themselves. This section will guide you through creating, managing, and getting the most out of these artifacts.
What Are Artifacts?
In the context of DOORS NG, an artifact is any piece of information that contributes to defining your project’s needs and deliverables. This broad definition encompasses everything from high-level business requirements to detailed system specifications. Artifacts are central to your project as they hold the critical information against which your project’s success will be measured.
Creating Artifacts
Step 1: Accessing the Artifact Creation Tool
- Navigate to the “Artifacts” section within your project dashboard. Here, you will find options to view existing artifacts or create new ones.
- Click on the “+ Create” or “New Artifact” button to begin the artifact creation process.
Step 2: Defining Your Artifact
- Name and Description: Give your artifact a clear, descriptive name and a detailed description. This practice ensures that anyone reviewing the artifact will immediately understand its purpose.
- Type: Select the type of artifact you’re creating, such as a “User Requirement,” “System Requirement,” “Test Case,” etc. The options available will depend on the project template you’ve chosen.
- Tags and Attributes: Assign tags for easy searching and filtering and fill out any additional attributes that could help categorize and define the artifact further, such as priority, status, or custom fields specific to your project’s needs.
Step 3: Organizing Artifacts
- Folders and Modules: Decide where your artifact will live within the project’s structure. You may place it within a specific folder for organizational purposes or within a module if you’re working with a set of related artifacts.
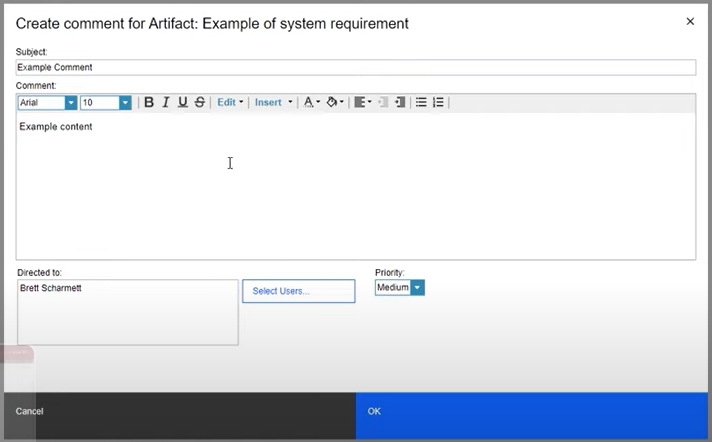
Managing Artifacts: Traceability and Collaboration
Traceability Links: One of DOORS NG’s strongest features is its ability to create traceability links between artifacts. Traceability links help you establish relationships, such as which high-level requirements are satisfied by which system requirements or which requirements are covered by specific test cases. Creating links is as simple as selecting two or more artifacts and using the “Link” option to define the relationship.
Collaboration: Encourage your team to engage with artifacts by adding comments, sharing insights, and contributing to discussions directly within DOORS NG. This collaboration feature ensures that all stakeholders can provide input, ask questions, and offer clarifications, enhancing the quality of your project requirements.
Leveraging Views for Data Display
As your project grows and the number of artifacts increases, finding ways to efficiently display and analyze this data becomes essential. DOORS NG offers customizable “Views” that allow you to filter, sort, and display artifacts based on various criteria:
- Creating Custom Views: Tailor artifact views by selecting which columns to display, such as name, status, assigned to, or any custom attributes you’ve defined. Save these views for quick access to see artifacts in a way that best suits your current task or focus area.
- Sharing Views: Share your custom views with team members to ensure everyone can access important information in a format that supports efficient workflow and decision-making.
Understanding and proficiently managing artifacts are key to harnessing the full potential of DOORS NG in your project’s requirements management process. By creating detailed, well-organized artifacts and leveraging DOORS NG’s collaboration and traceability features, you’ll build a solid foundation for a successful project outcome.
Advanced Features: Linking and Traceability
Mastering the core aspects of DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG) provides a robust foundation for managing your project’s requirements. However, the true power of DOORS NG unfolds when you start leveraging its advanced features, particularly linking and traceability. This section dives into how creating links between artifacts can elevate your project’s organization, ensuring that every team member understands how different parts of the project interconnect.
Understanding Traceability
Traceability in DOORS NG is the mechanism that allows you to establish and visualize relationships between artifacts. It’s a critical component for ensuring that requirements are met throughout every phase of the project, from initial planning to final testing and validation. Traceability offers several benefits:
- Impact Analysis: Quickly ascertain the implications of changing a requirement by understanding all related dependencies.
- Coverage: Ensure all requirements have corresponding test cases and that no aspect of the project is overlooked.
- Compliance: Demonstrating to stakeholders how requirements are fulfilled throughout the project lifecycle.
Creating Links between Artifacts
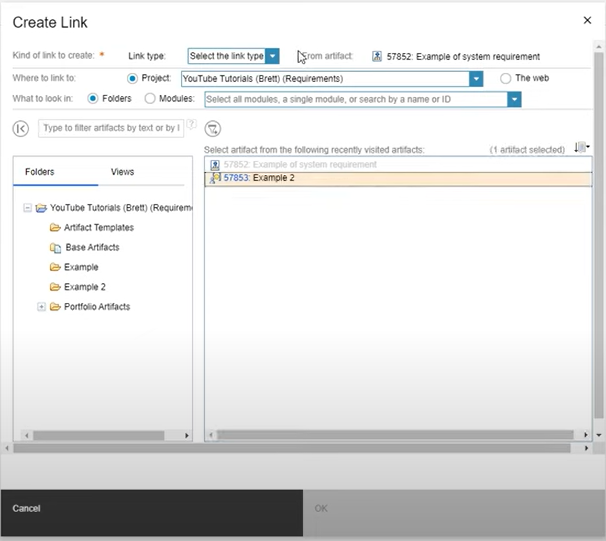
Linking is the action of creating traceability between artifacts. Follow these steps to create your first links:
Step 1: Select Your Artifacts
Navigate to the “Artifacts” section of your project and choose the items you want to link. This can be as simple as linking a high-level requirement to more detailed system requirements or associating a requirement with its corresponding test cases.
Step 2: Initiate the Linking Process
With your artifacts selected, look for the “Link” option. This might manifest as a button or a right-click context menu, depending on where you are in DOORS NG. Clicking this opens the linking interface.
Step 3: Define the Relationship
Within the linking interface, you’ll specify the nature of the relationship between the selected artifacts. DOORS NG supports various link types, such as “Satisfies”, “Validated by”, or custom types defined within your project. Selecting the appropriate link type clarifies how the artifacts relate to one another.
Step 4: Finalize the Link
After choosing the link type and ensuring both artifacts are correctly selected, finalize the link. Once created, the link becomes a visual representation of the relationship, often viewable in traceability matrices or reports within DOORS NG.
Utilizing Traceability Views and Matrices
With linking in place, utilizing traceability views and matrices enables you to visualize the project’s interconnectedness. These tools aggregate your linked artifacts, offering a comprehensive overview of relationships and dependencies.
Traceability Matrices: A powerful feature within DOORS NG, traceability matrices display the relationships between artifacts across two axes. For example, you can see which system requirements are satisfied by which high-level business requirements, providing a snapshot of coverage and compliance.
Custom Traceability Views: Tailor traceability views to focus on specific project dimensions. You might create views that highlight test coverage, showing directly which requirements have corresponding test cases and the status of those tests. Custom views are particularly beneficial for reporting to stakeholders or during project reviews, as they can be designed to target the information most relevant to your audience.
Best Practices for Managing Links
- Consistent Link Types: Use link types consistently across the project to maintain clarity. Standardizing on a set of link types helps team members understand the relationships at a glance.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review your links and the overall traceability structure to ensure it’s updated with the project’s progress. This can involve verifying that all requirements are linked to their implementations and tests, and updating links as the project evolves.
- Link Documentation: While links themselves provide a direct relationship between artifacts, adding comments or rationale to a link can provide context that’s invaluable during retrospectives or audits.
Harnessing the linking and traceability features of DOORS NG transforms the way teams manage projects. It not only streamlines compliance and impact analysis but also deepens the understanding of how each project element supports the overarching goals. As you become more adept at utilizing these advanced features, your ability to navigate complex projects with confidence will significantly enhance.
With a firm grasp on creating and managing artifacts, and leveraging the powerful linking and traceability features of DOORS Next Generation (DOORS NG), you’re well on your way to mastering this comprehensive requirements management tool. However, efficiently navigating within DOORS NG can further optimize your workflow, ensuring you make the most out of this robust platform. This section delves into advanced tips and strategies for seamless navigation and artifact management.
Efficient Searching and Filtering
As your project grows, so does the volume of artifacts, making efficient searching and filtering capabilities indispensable.
- Utilize Advanced Search: Learn to use the advanced search feature, which allows you to query artifacts based on text, tags, attributes, or custom queries. This feature can significantly reduce the time spent looking for specific information.
- Bookmarking: DOORS NG allows you to bookmark frequently accessed artifacts, folders, or views. Leveraging bookmarks ensures you can quickly navigate to essential parts of your project without sifting through the entire project hierarchy.
- Custom Filters: Beyond using pre-defined views, creating custom filters based on artifact attributes or your custom tags can streamline your workflow, allowing you to focus only on the artifacts that require attention at any given time.
Leveraging the Dashboard for Quick Access
Your dashboard is not just a place for widgets; it’s your command center for accessing all areas of your project quickly.
- Widget Customization: Beyond the basic widgets, explore DOORS NG’s widget library for options that can provide quick insights or access to different project areas. This might include widgets for recent changes, artifact reviews, or test execution results.
- Layout Optimization: Regularly review and optimize your dashboard layout to match your current project phase. For instance, during the initial phases, you might focus more on high-level requirements and design specifications. In contrast, later stages might require quick access to test cases and validation results.
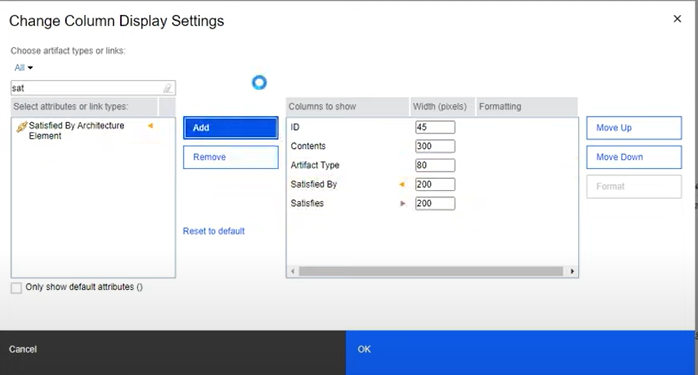
Advanced Artifact Management
Mastering artifact management involves not just creating and linking but also ensuring that your artifacts remain organized and maintainable throughout the project lifecycle.
- Regular Audits: Perform regular audits of your artifacts to ensure they are up-to-date and accurately reflect the current state of your project. This includes reviewing artifact statuses, updating descriptions, and verifying links.
- Version Control: Make use of DOORS NG’s version control capabilities to track changes over time. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your project’s requirements and understanding the
rationale behind changes. - Archiving: For completed projects or obsolete artifacts, utilize the archiving feature to keep your active project area clean and focused while still retaining access to historical data if needed.
The Path Forward: Continuing Your DOORS NG Journey
As you become more comfortable with DOORS NG, exploring its full suite of features and capabilities will be both rewarding and beneficial to your projects. Embrace the following strategies as you continue your journey:
- Continuous Learning: DOORS NG is a deep and complex tool; continuous learning is key. Take advantage of IBM’s tutorials, documentation, and community forums to stay up-to-date on best practices and new features.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage feedback from your team on the DOORS NG setup and workflow. Collaborative improvement can lead to more efficient use of the tool and a smoother project management process.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Explore integrations with other tools in the IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management suite or third-party tools your team uses. Integrations can streamline workflows and enhance collaboration.
By following these advanced tips and strategies, embracing continuous learning, and fostering a culture of feedback and improvement, you’re well-equipped to leverage DOORS Next Generation to its fullest potential. Whether you’re managing straightforward projects or navigating the complexities of large-scale engineering endeavors, DOORS NG offers the tools and flexibility needed to ensure success.
Thank you for joining this beginner’s journey into DOORS NG. Your path toward mastering requirements management with one of the industry’s leading tools has just begun. Remember, the complexity of DOORS NG is matched by its power and versatility. Embrace the challenge, and you’ll find that your projects run smoother, with outcomes that meet or exceed your expectations.